Please note that the procedures outlined in this guide pertain to connecting an S3 bucket and LABELLERR within the same AWS account.
Prerequisites
- AWS Account: You must have an active AWS account to access and utilize the IAM service. If you don’t have an account, you can sign up for one at the AWS website.
- IAM Permissions: Ensure that you have the necessary permissions to create IAM users and policies. You need to have IAM administrative access or consult with your AWS account administrator to grant you the required permissions.
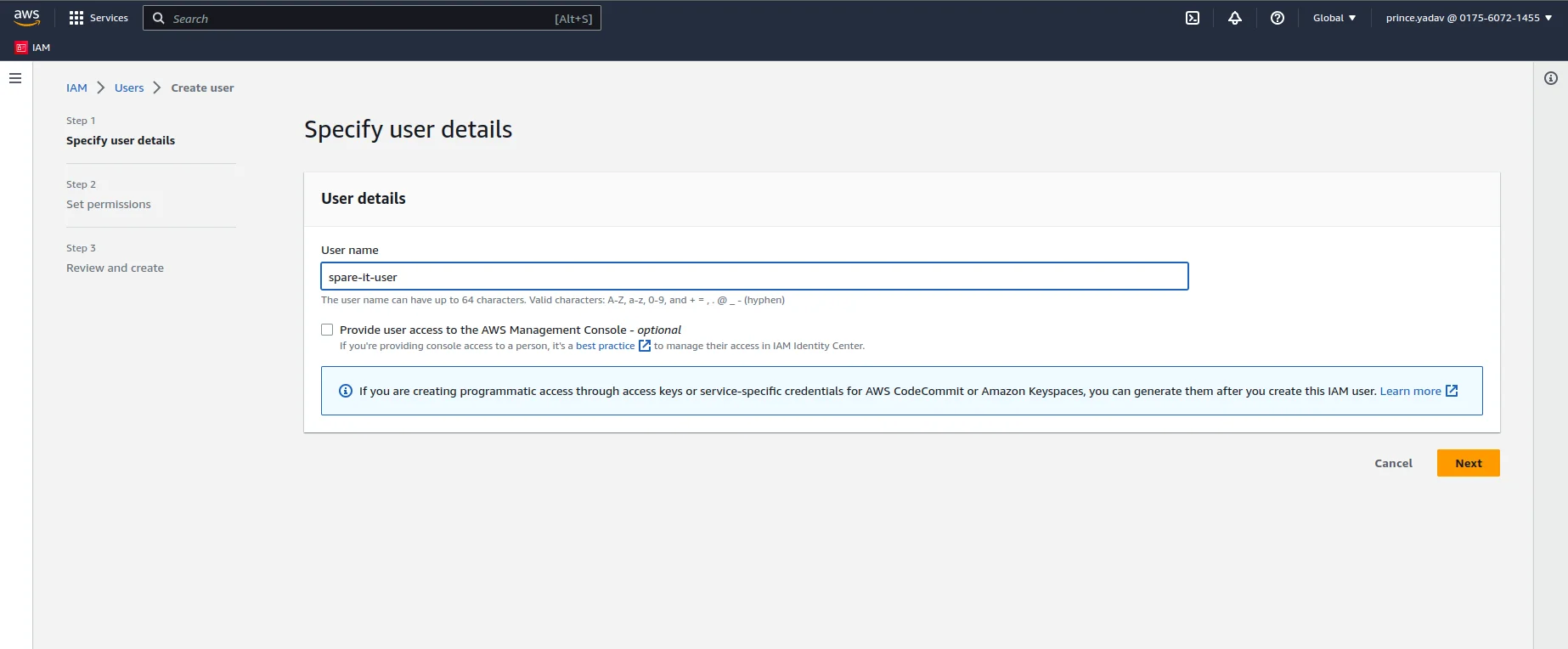
- IAM User Creation: Decide on the user(s) you want to create in IAM. Consider the appropriate naming conventions and the level of access each user should have. Determine the number of users you need to create and the specific roles and permissions they require.
- User Credentials: Plan how you will manage the user credentials. Determine whether you will generate initial passwords for the users or require them to set their own passwords upon first login. Alternatively, you can leverage AWS Single Sign-On or other authentication mechanisms.
- IAM Policies: Identify the specific permissions and access levels required for each user. You can create custom policies to grant fine-grained permissions or leverage existing AWS managed policies. Define the policies that align with your security and access control requirements.
- IAM Best Practices: Familiarize yourself with IAM best practices, such as implementing the principle of least privilege, regularly reviewing and rotating credentials, and enabling multi-factor authentication (MFA) for added security.
Quick Reference
S3 URI Format
S3 Path Format
Required Permissions Summary
- Import (Read)
- Export (Write)
| Permission | Purpose |
|---|---|
s3:GetObject | Read files from bucket |
s3:ListBucket | List bucket contents |
s3:GetBucketCors | Get CORS configuration |
s3:GetBucketLocation | Get bucket region |
s3:PutBucketCors | Set CORS policy (or configure manually) |
CREATE IAM USER
Set Permissions
In the Set Permissions section you will see the Permissions options. Choose Attach Policies Directly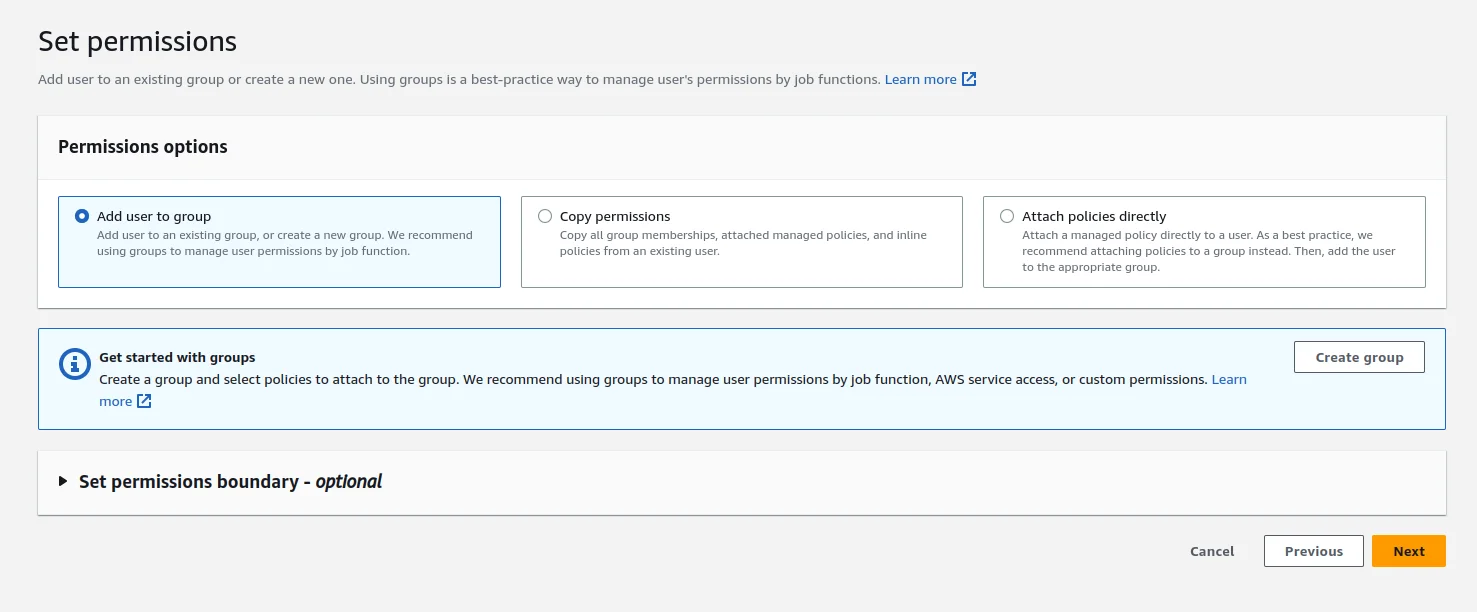 After choosing the above option you can see the list of existing policies
After choosing the above option you can see the list of existing policies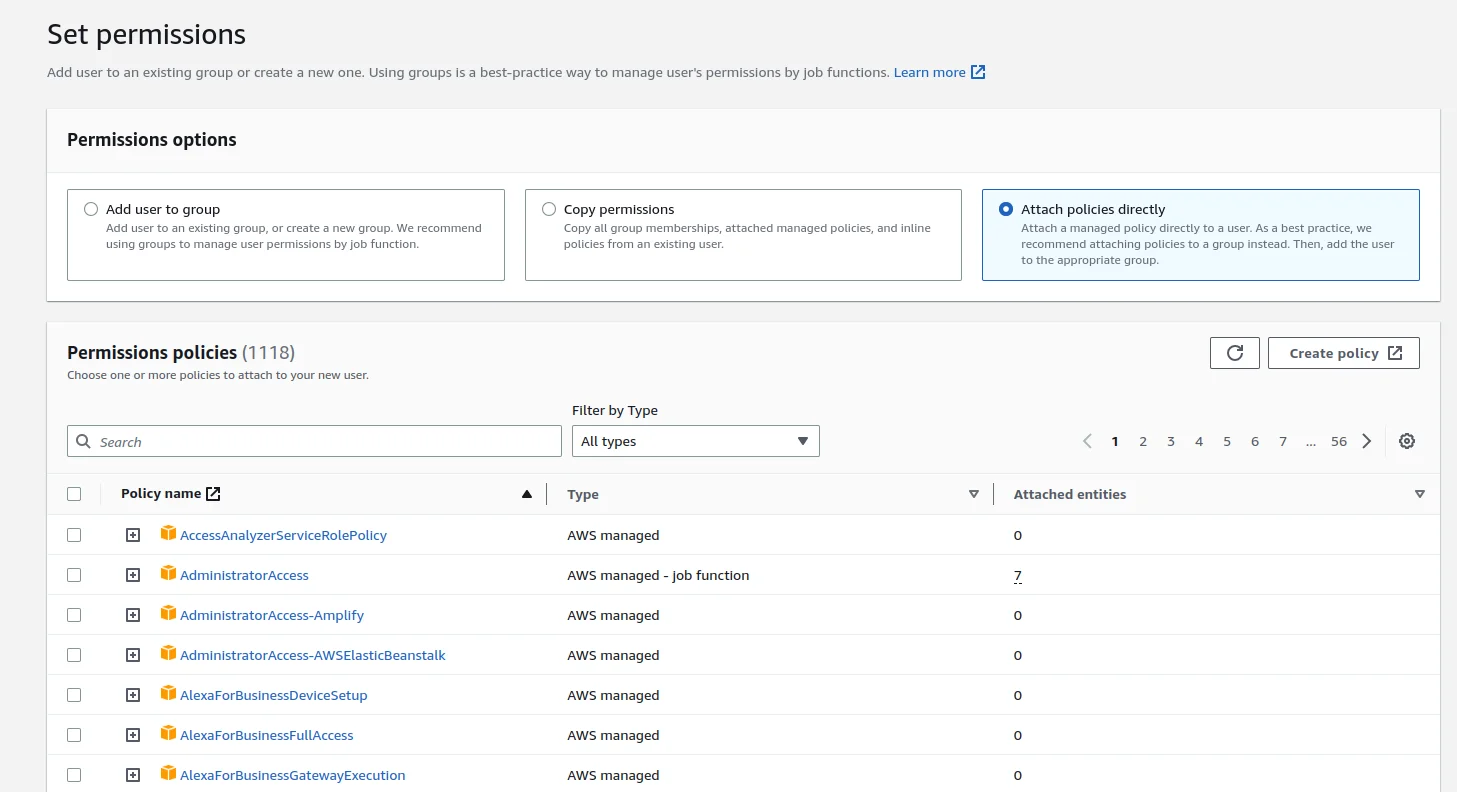


Create Custom Policy
Create a new policy for the user to access the bucket. Now click on the Create policy button. After this you will be redirected to a window IAM ⇒ Policies ⇒ Create Policy as we can see following.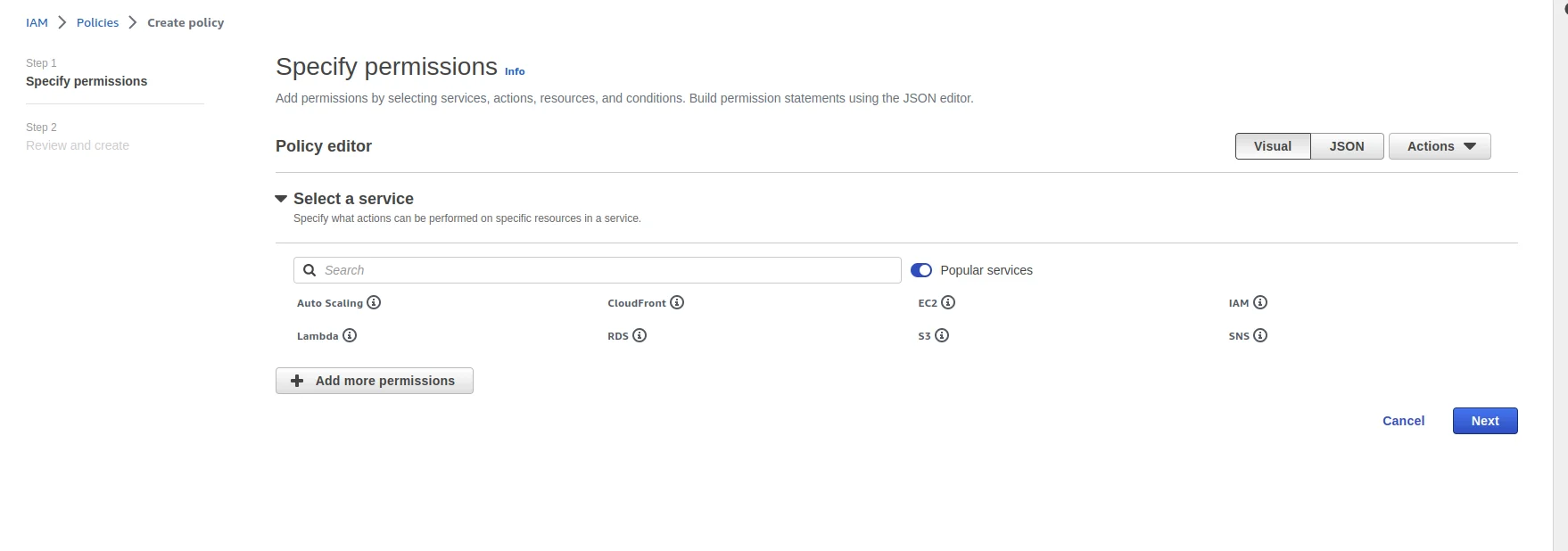 Choose the JSON option from the RIGHT-HAND-SIDE of the window. After choosing the JSON option you will see the window as follow
Choose the JSON option from the RIGHT-HAND-SIDE of the window. After choosing the JSON option you will see the window as follow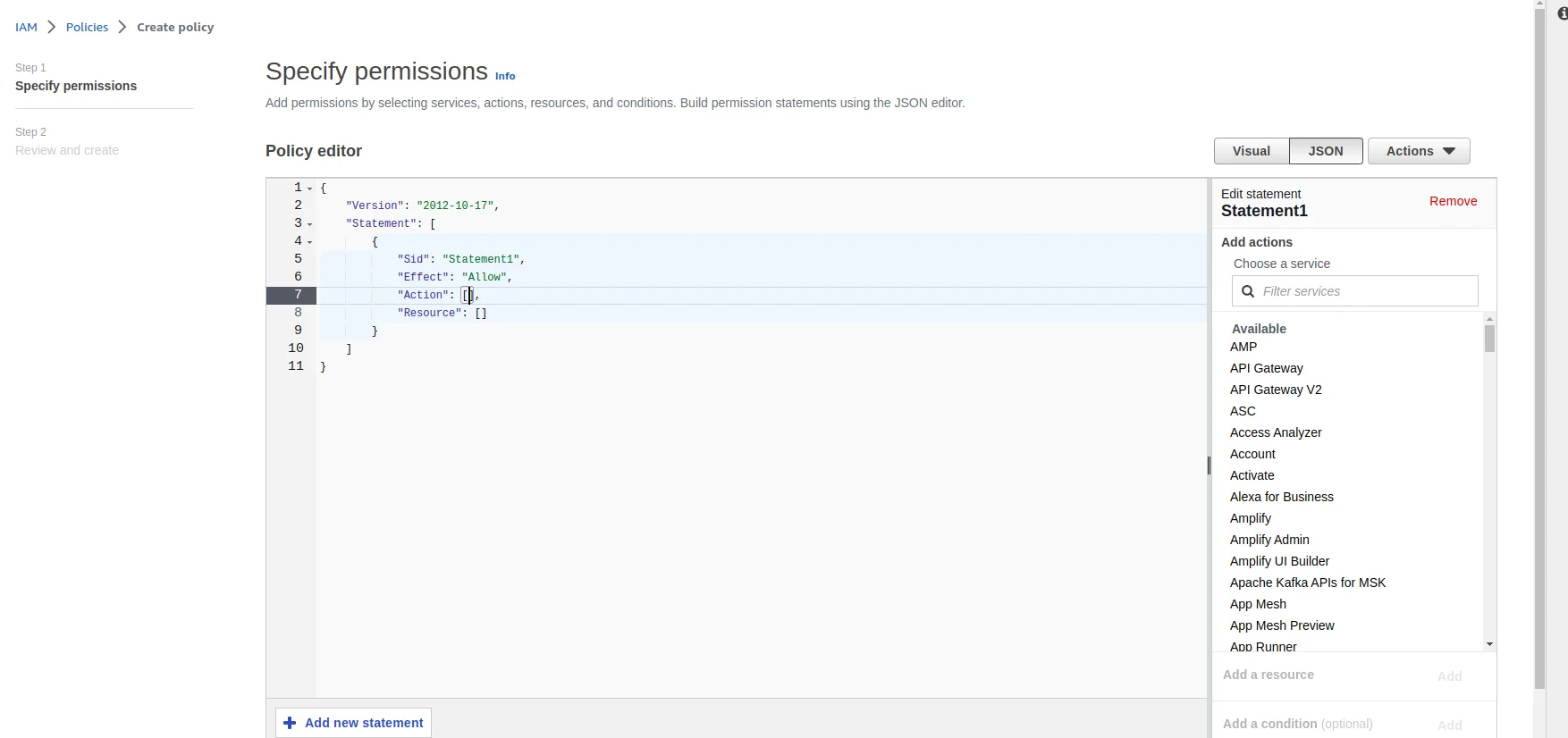


Configure Policy Permissions
Update the JSON as follow and replace the your-bucket-name with bucket-name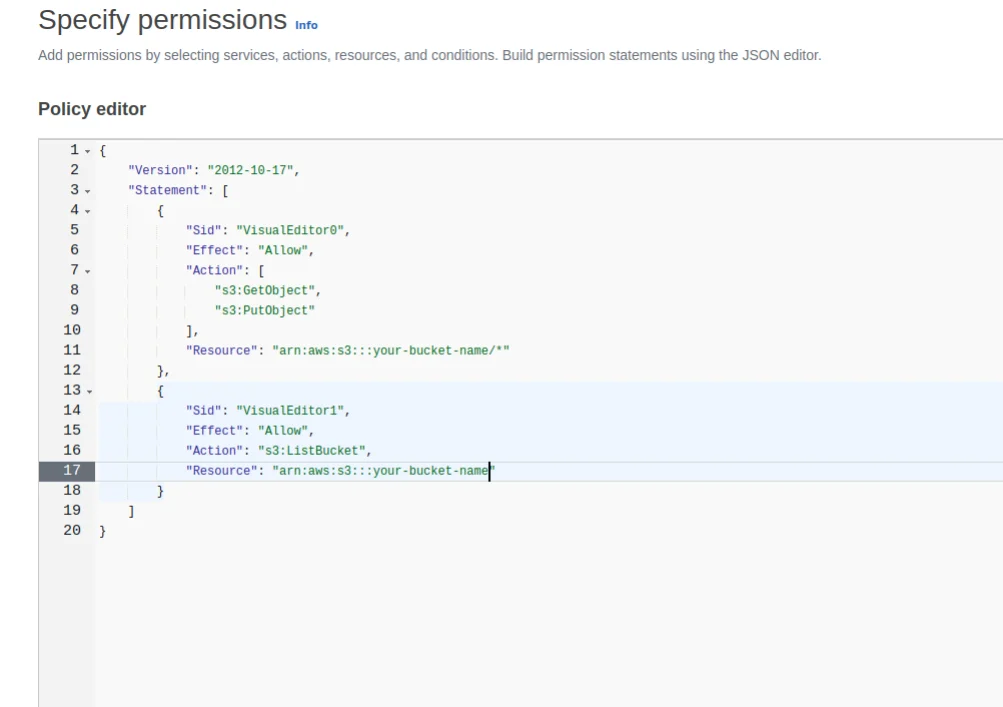 Now, update the JSON policy. We will create two permission sets: one for importing data from S3 and another for exporting data to S3.
Now, update the JSON policy. We will create two permission sets: one for importing data from S3 and another for exporting data to S3.

A. Policy for Importing Data
To allow Labellerr to read data from your bucket, paste the following JSON code. Replaceyour-bucket-name with the actual name of your S3 bucket.Note: If you prefer not to grant
s3:PutBucketCors permission, you can set the CORS policy on your S3 bucket manually with the following configuration. For more details, refer to the official AWS documentation on CORS.B. Policy for Exporting Data
To allow Labellerr to write (export) annotations back to your S3 bucket, add the following permissions to your policy. These are required in addition to the import permissions above.Finalize Policy
Click on Next button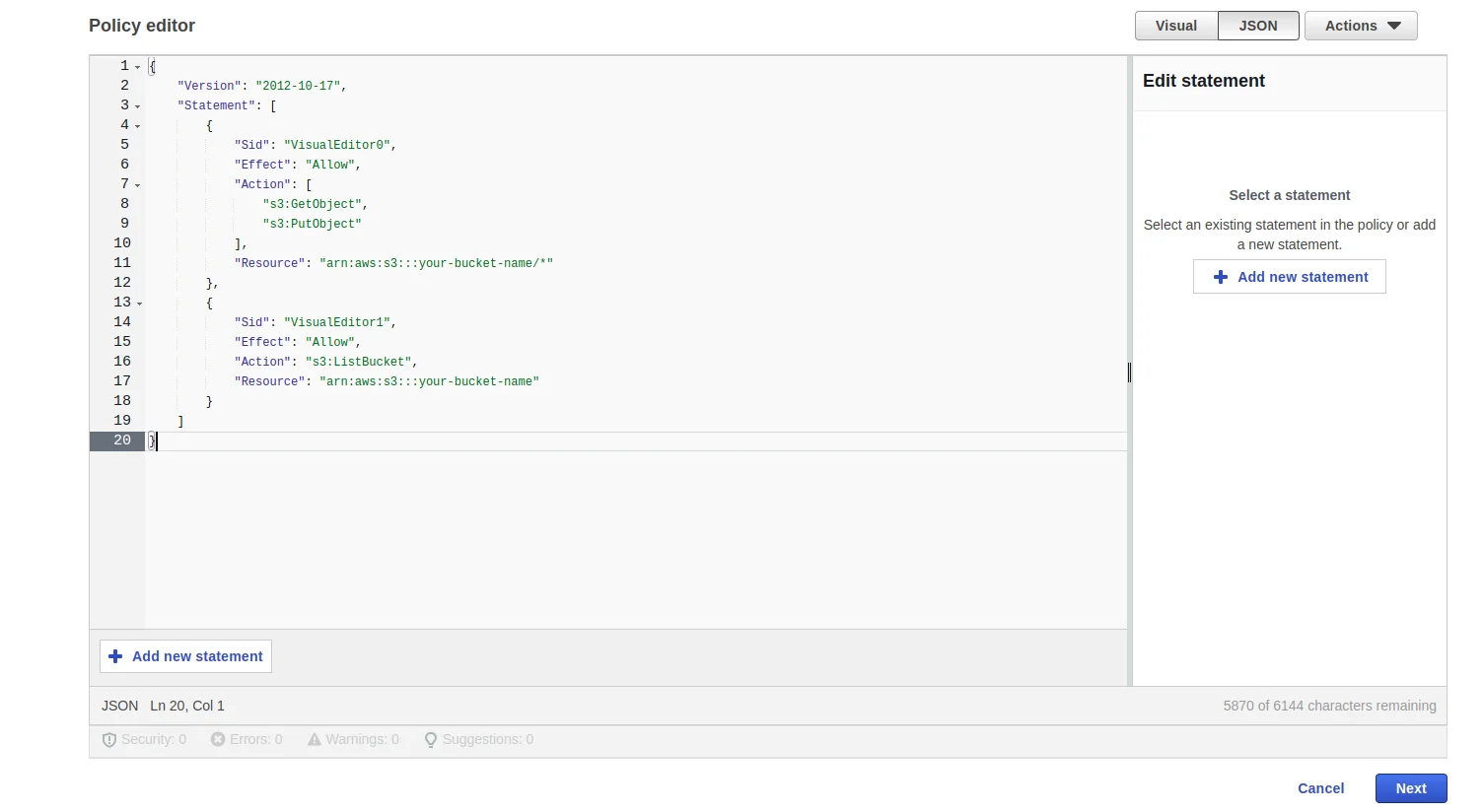 Fill the Policy name & Policy Description and click on Create policy button
Fill the Policy name & Policy Description and click on Create policy button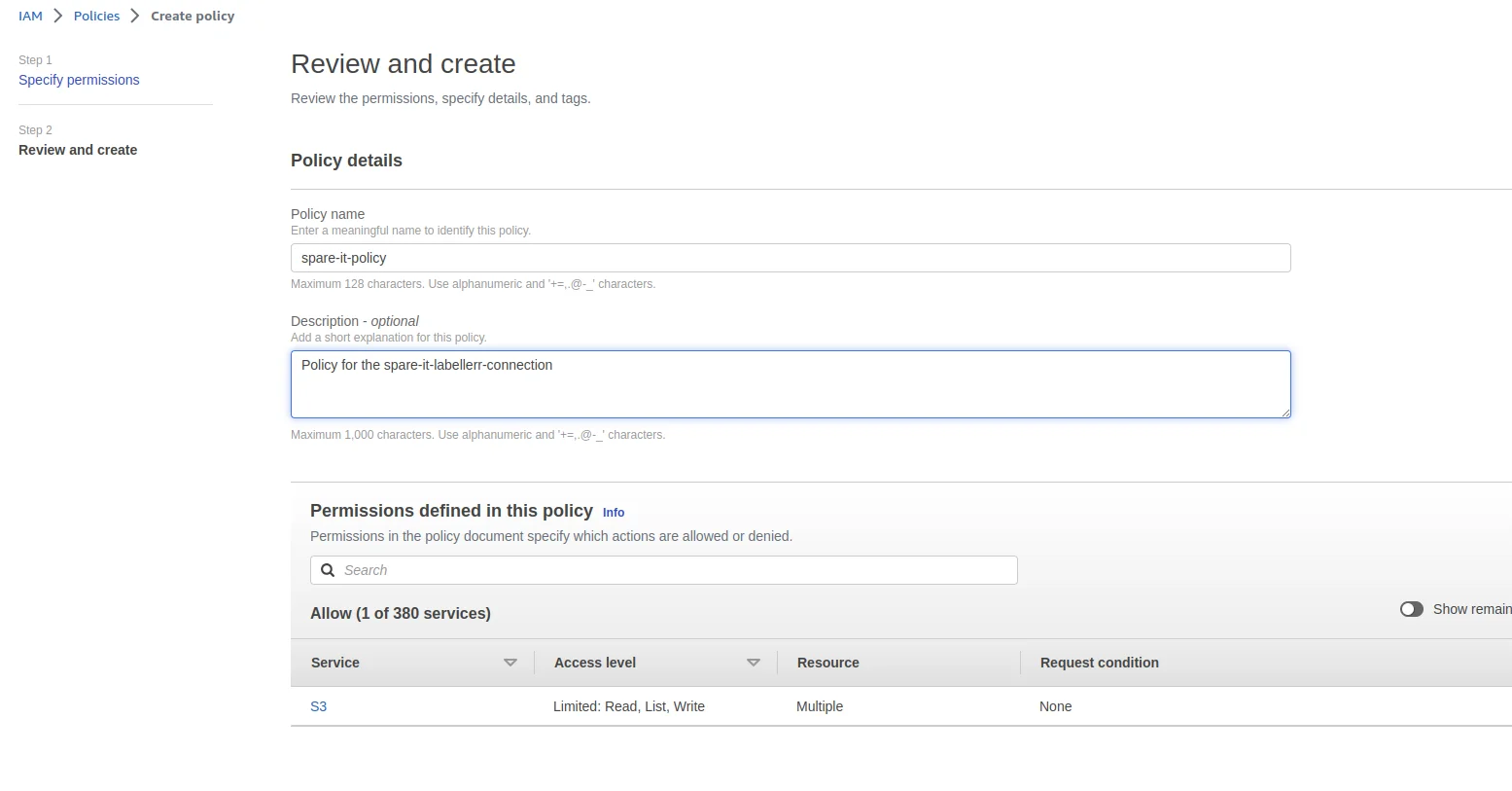
 After this the policy will be created and listed
After this the policy will be created and listed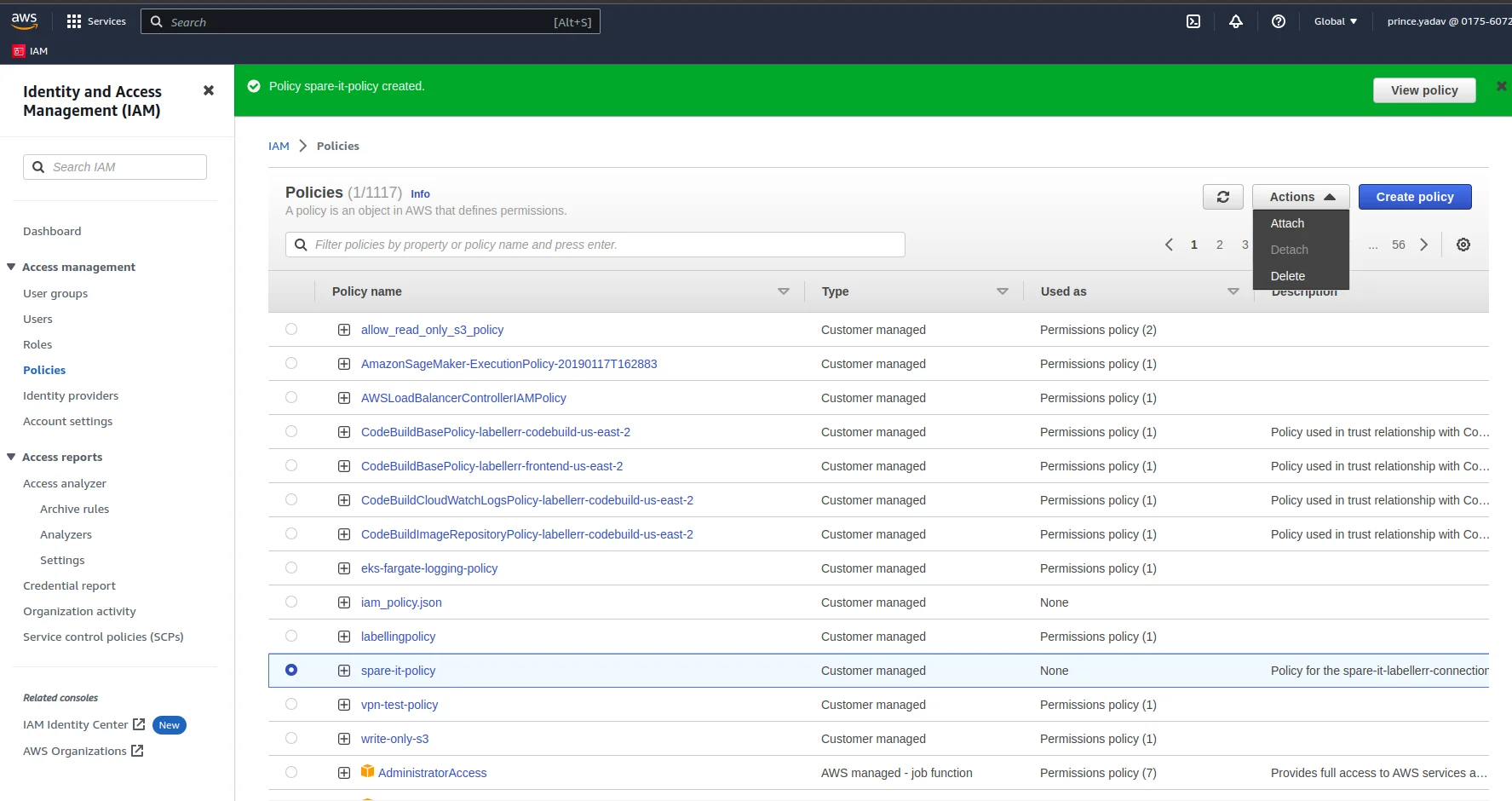




Attach Policy to User
Now go to the previous user-creation window and after reloading and entering the User Name and selecting the option Attach policies directly we can see the policy that we created. Choose the same policy and click on Next button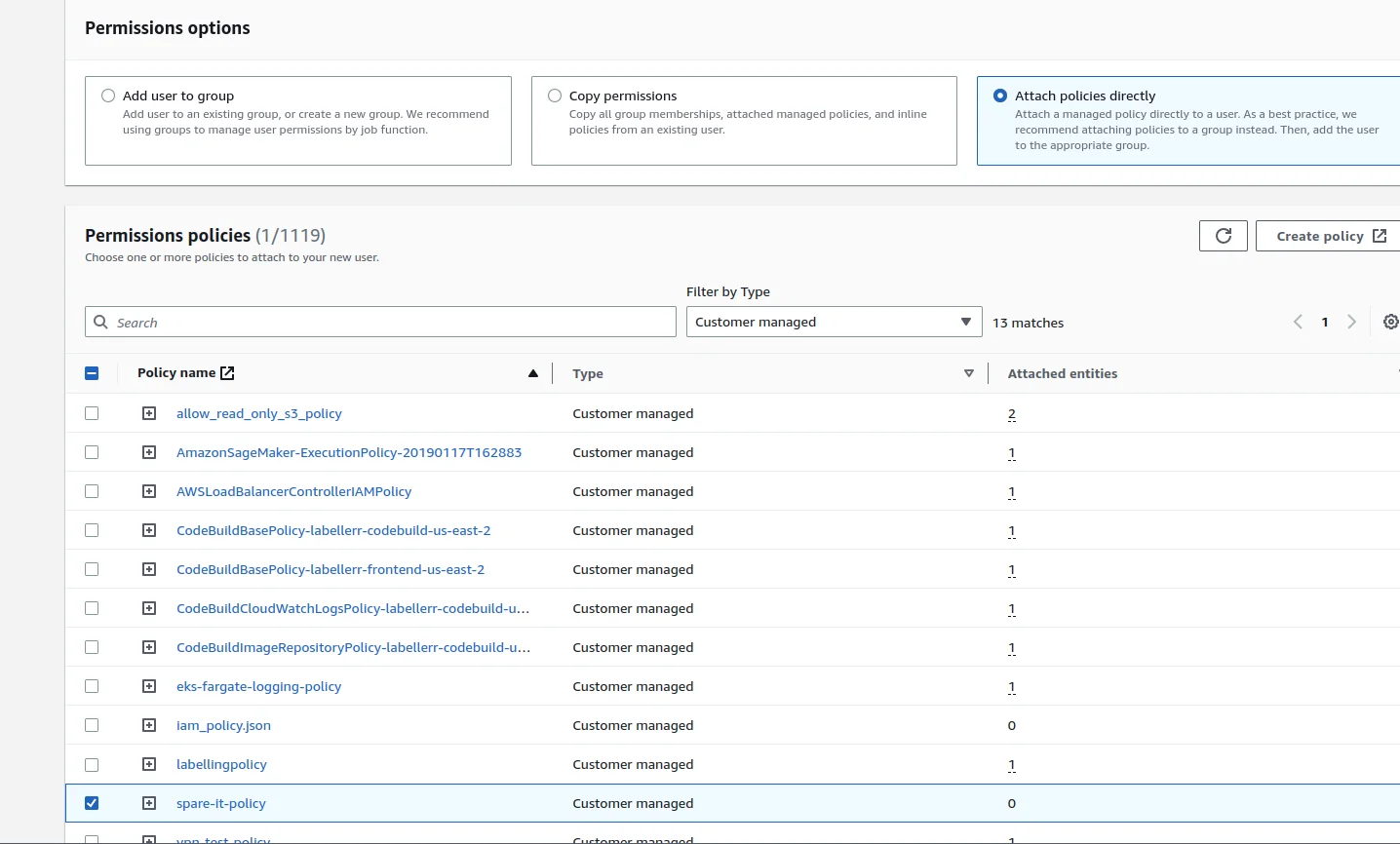
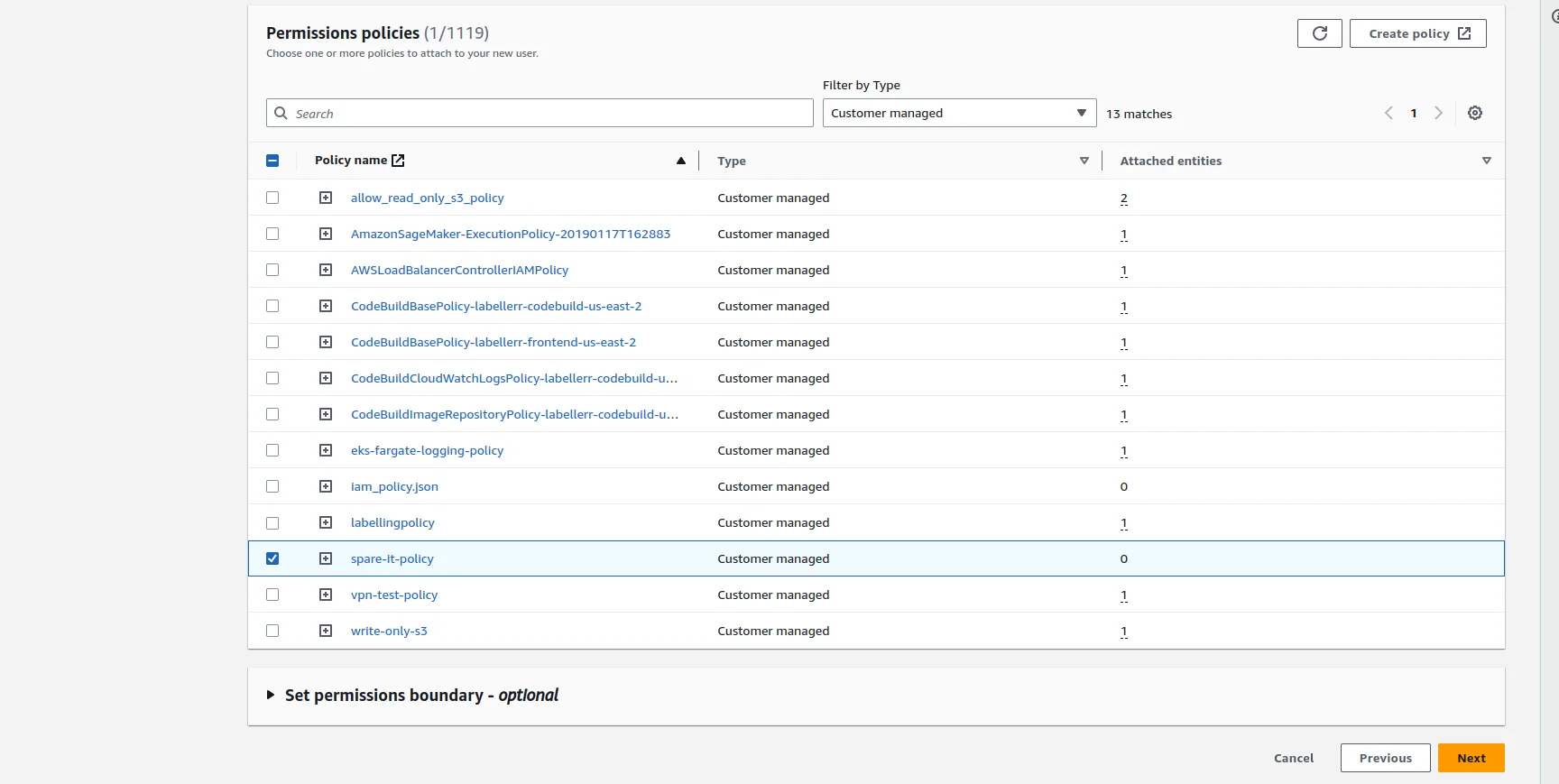 Now click on Create user button and user will be created
Now click on Create user button and user will be created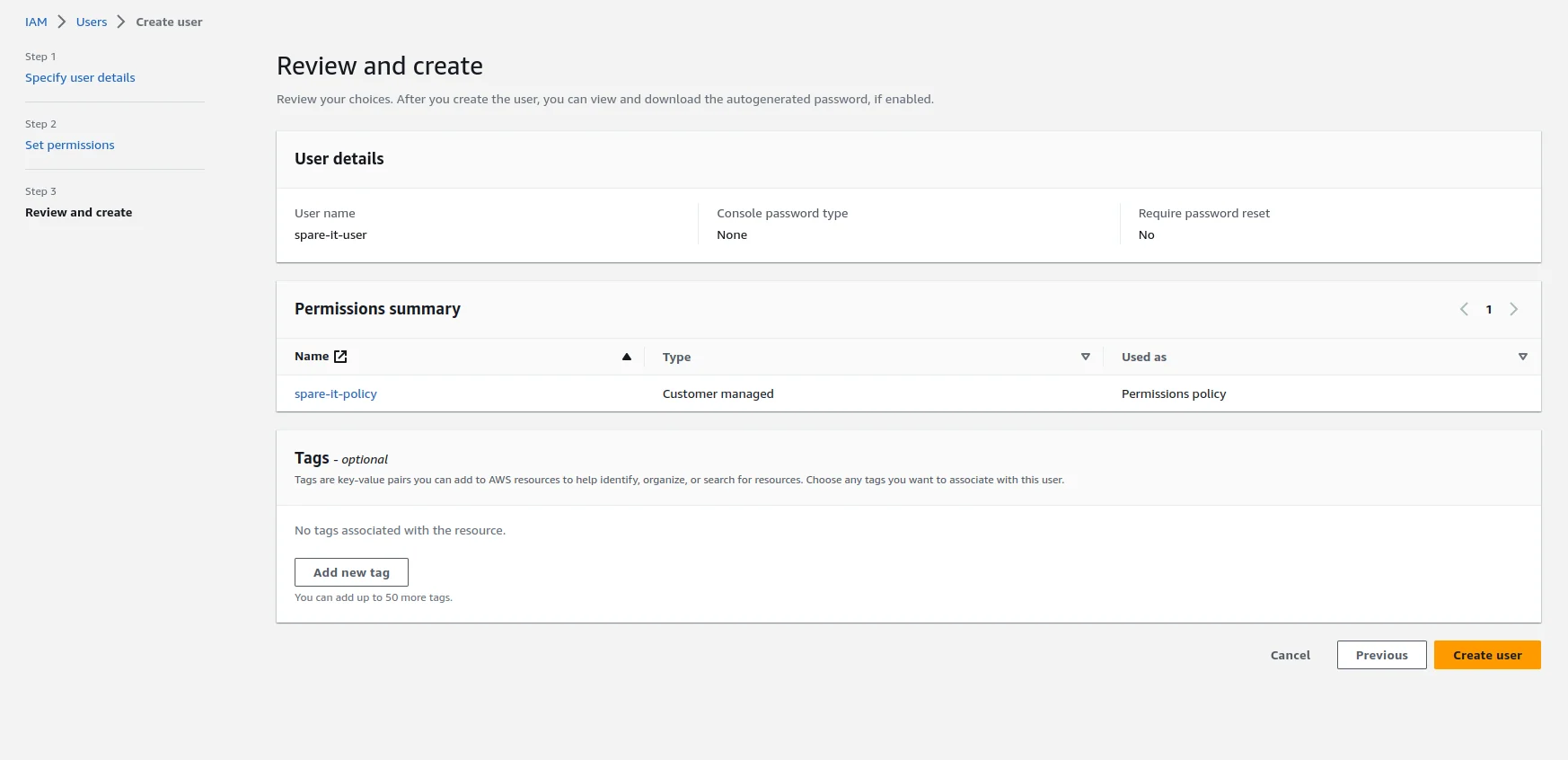




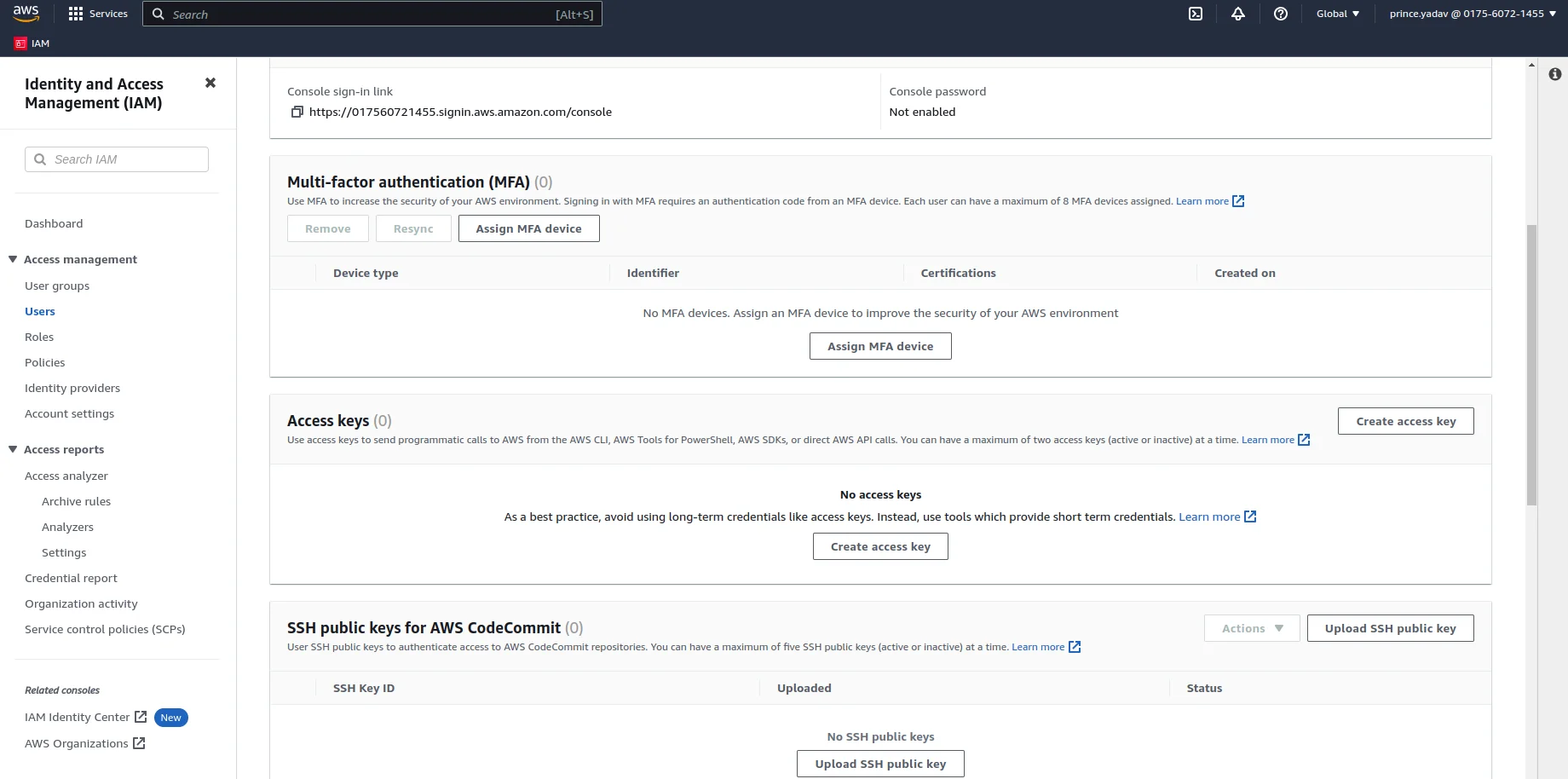
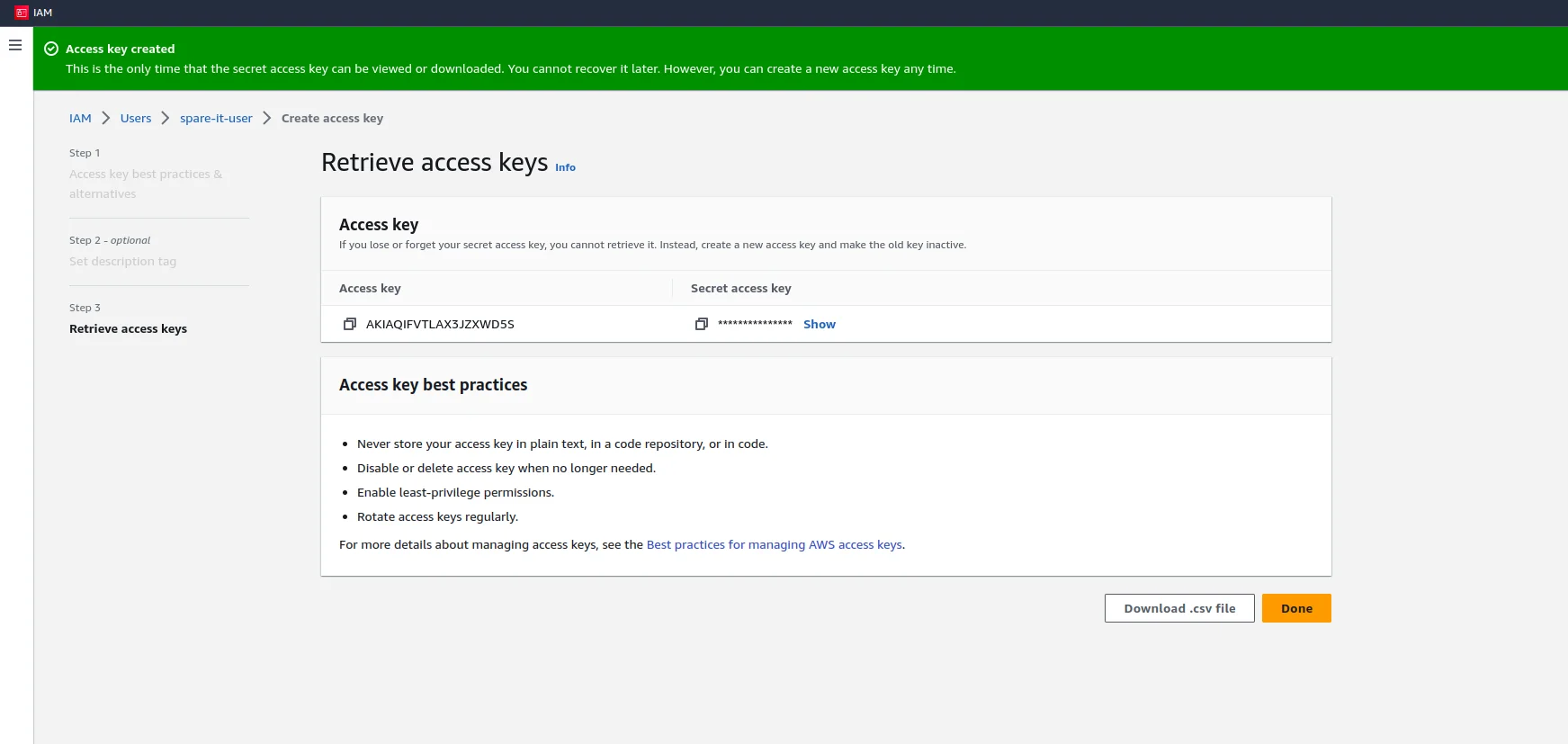
Generate Access Key
Creating Dataset & Annotation Project at LABELLERR
Select Amazon S3
While creating a project dataset choose Amazon S3 to connect data-source and click on Create new connection button.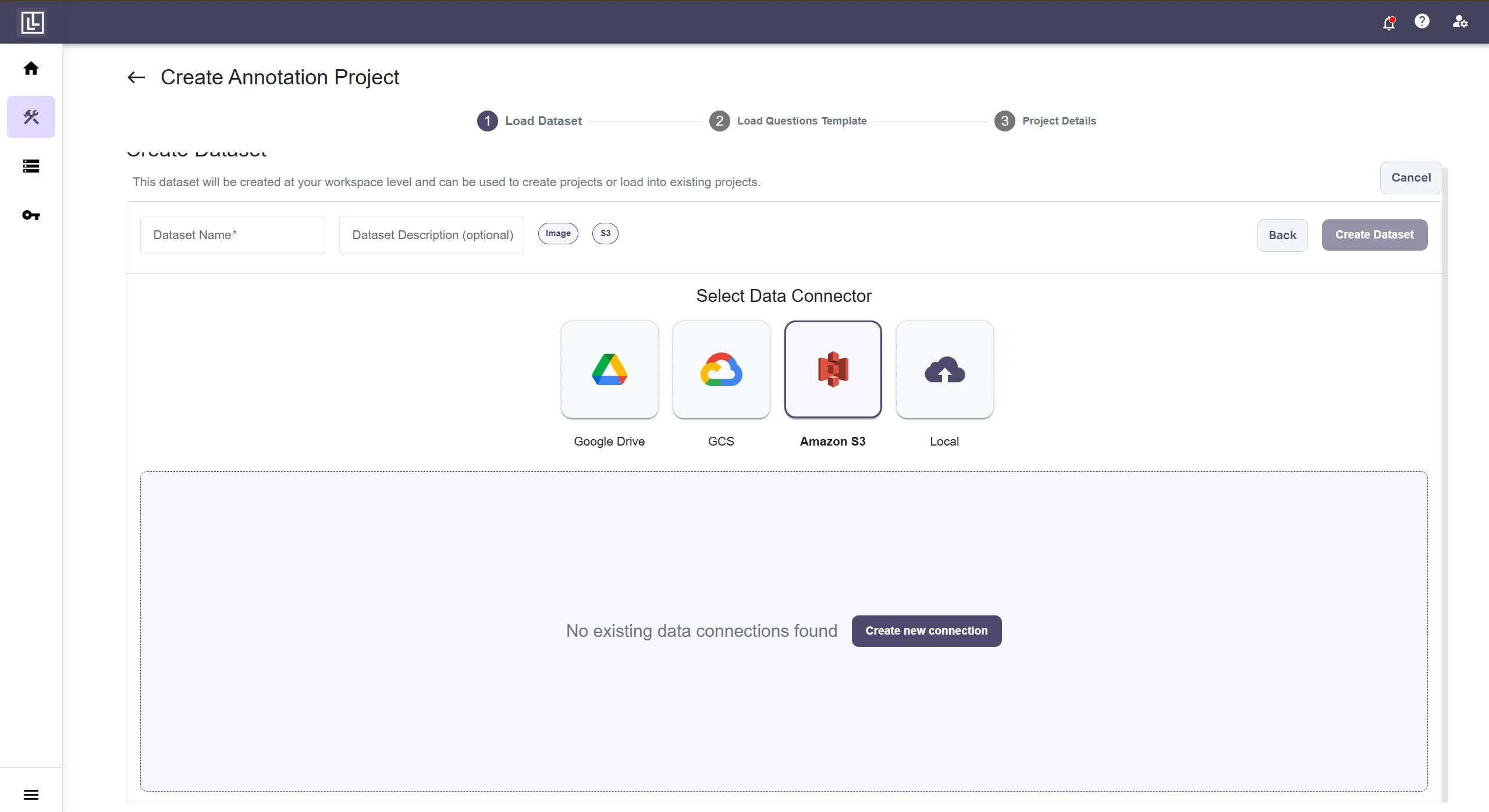

Configure Connection
Fill in the details. Fill the Access key & Secret Access Key generated in previous steps along with s3 URI. To find the s3 URI go to your bucket and copy the path of the images folder. Also remove the s3:// prefix from the URL. Now click on connect button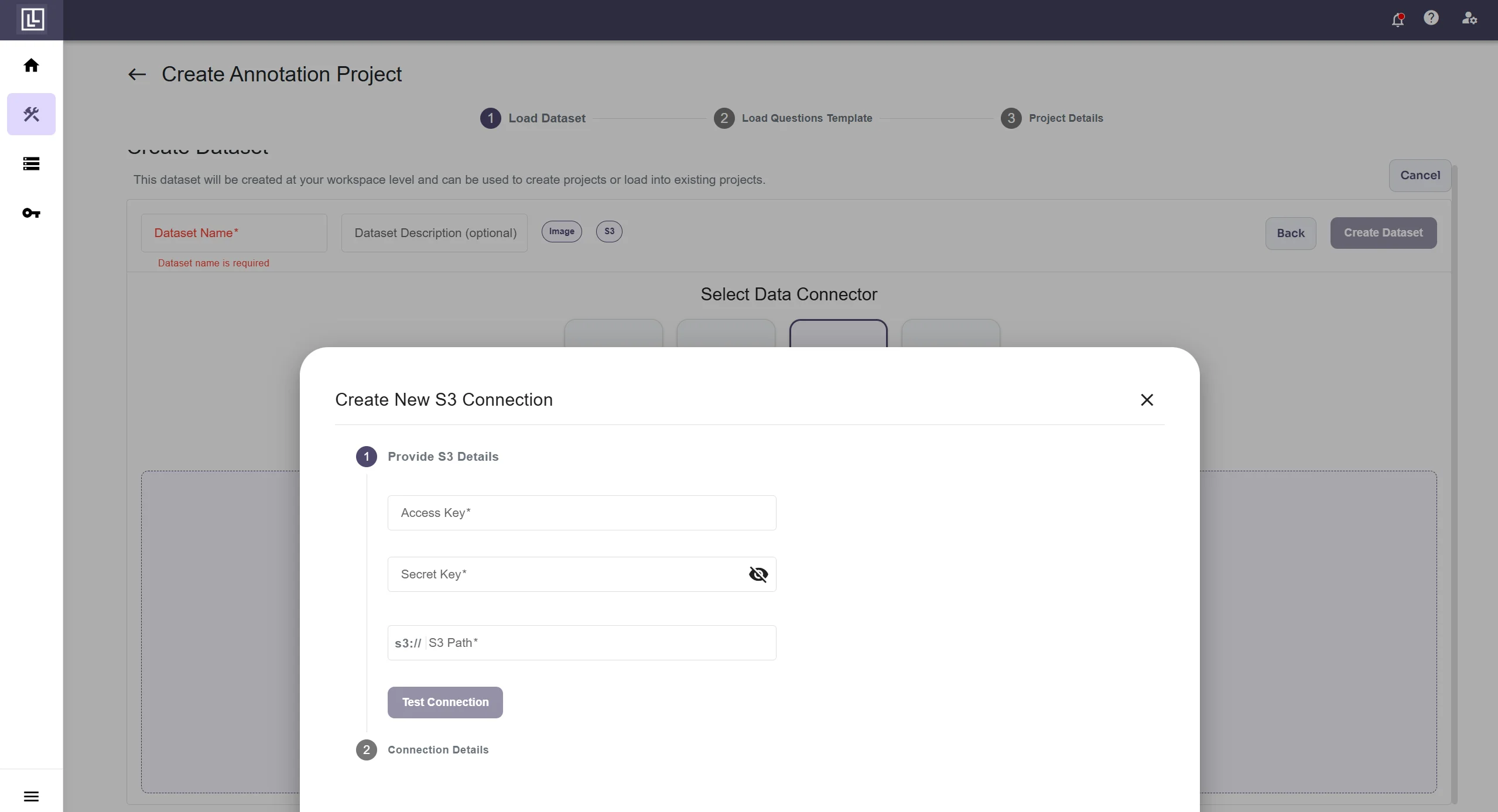 If you fill in the details correctly you will receive this message.
If you fill in the details correctly you will receive this message.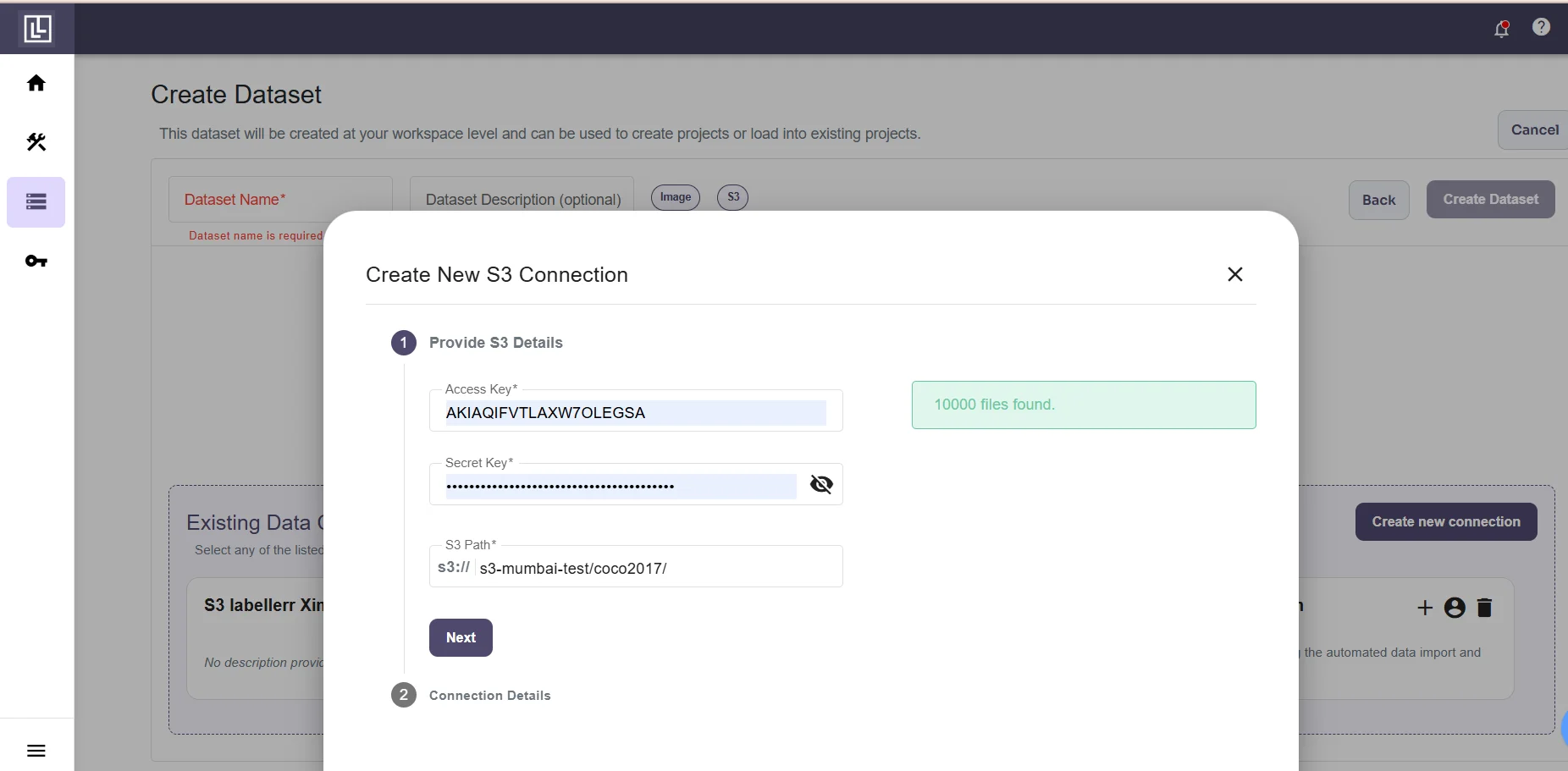 If you messed up somewhere you will get an error.
If you messed up somewhere you will get an error.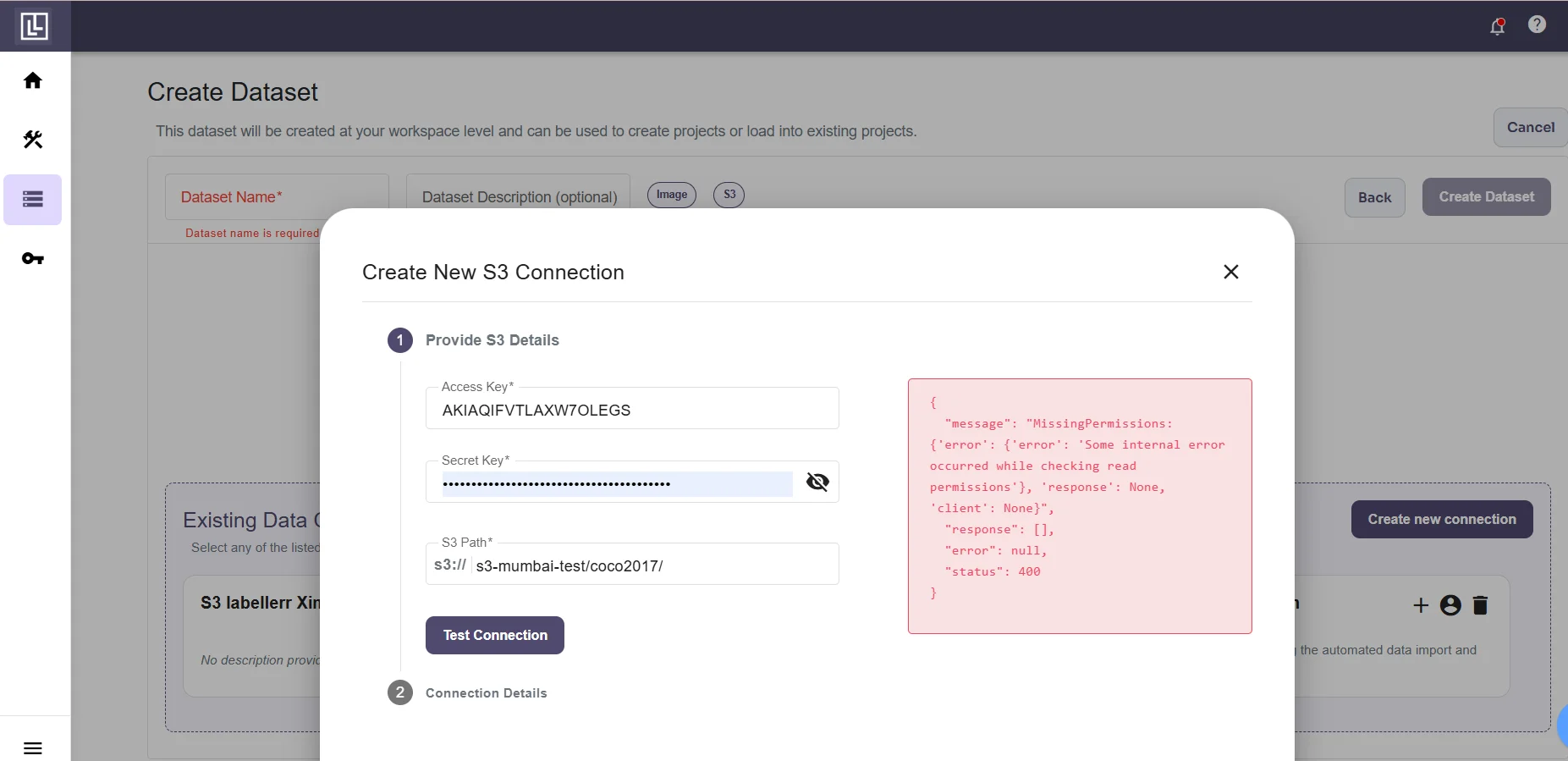 After successfully testing the connection you will be required to fill the Connection Name and Connection Description(Optional).
After successfully testing the connection you will be required to fill the Connection Name and Connection Description(Optional).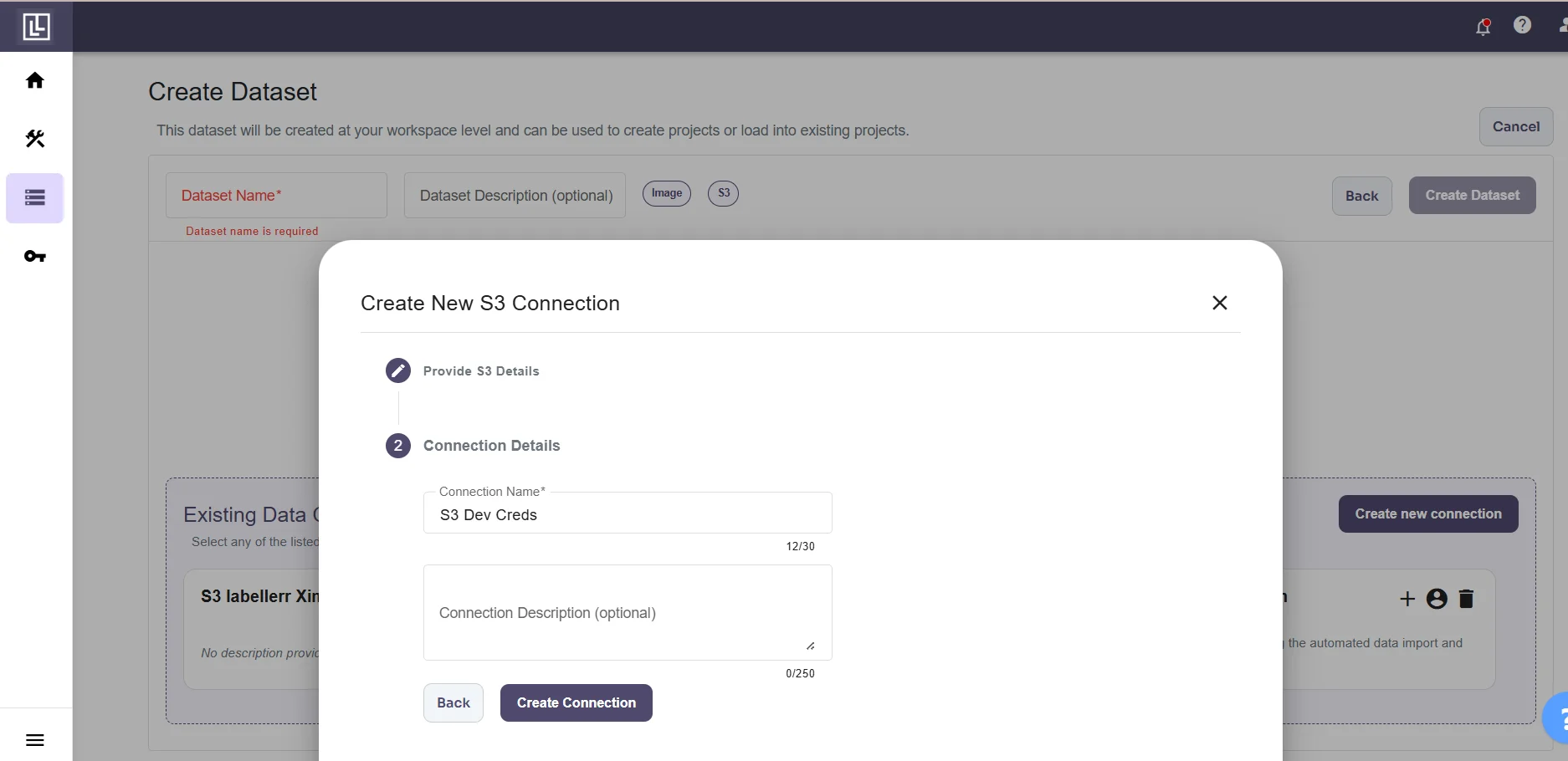




Troubleshooting
Dataset creation shows status 500 or 'Failed'
Dataset creation shows status 500 or 'Failed'
Symptom: Dataset appears to create successfully but then shows “Failed” status or status code 500.Cause: The IAM user/connection does not have the required permissions to access the S3 bucket.Solution:
- Verify the IAM policy is correctly attached to your user
- Ensure the bucket name in the policy matches your actual bucket
- Check that the
/*wildcard is included for object-level permissions - Test the connection before creating datasets:
'Dataset has no files' error
'Dataset has no files' error
Symptom: Files exist in S3 bucket but dataset shows 0 files.Cause: The connection lacks read permissions (
s3:GetObject, s3:ListBucket) on the bucket.Solution:- Verify
s3:GetObjectpermission is set on the bucket objects (arn:aws:s3:::bucket-name/*) - Verify
s3:ListBucketpermission is set on the bucket (arn:aws:s3:::bucket-name) - Check that the path format is correct:
s3://bucket-name/folder/
Connection test fails
Connection test fails
Symptom: Connection test returns an error when trying to connect.Cause: Invalid credentials, wrong path format, or insufficient permissions.Solution:
- Verify your Access Key and Secret Access Key are correct
- Check the path format:
s3://bucket-name/path/to/folder/ - Ensure the IAM user has all required permissions listed above
- Verify the bucket exists and is in the correct AWS region
CORS errors in browser
CORS errors in browser
Symptom: Images don’t load in the Labellerr annotation interface due to CORS errors.Cause: Missing CORS configuration on the S3 bucket.Solution:
Either grant
s3:PutBucketCors permission to allow Labellerr to set CORS automatically, or configure CORS manually on your bucket:'No files found with status' during export
'No files found with status' during export
Symptom: Export fails with “No files found with the given status” error.Cause: Files have not been moved to the expected workflow stage (review, client_review, or accepted).Solution:
- Ensure files have been annotated AND reviewed before exporting
- Check the
statusesparameter in your export configuration - Valid statuses for export:
review,client_review,accepted
Internal server error with tracking ID
Internal server error with tracking ID
Symptom: An “Internal server error” appears with a tracking ID.Cause: Usually indicates a server-side issue, often related to permissions.Solution:
- Note the tracking ID for support reference
- Check connection permissions are still valid
- Verify IAM user credentials haven’t been rotated or revoked
- Contact support@tensormatics.com with the tracking ID